
Gas chromatography (GC) is an analytical technique applicable to gas, liquid, and solid samples (components that are vaporized by heat). If a mixture of compounds is analyzed using a GC system, each compound can be separated and quantified.
Principle of gas chromatography
The sample solution injected into the instrument enters a gas stream which transports the sample into a separation tube known as the "column." (Helium or nitrogen is used as the so-called carrier gas.) The various components are separated inside the column.
- Medicine. GC-MS is used in screening tests for the detection of several congenital metabolic diseases. ...
- Environmental Monitoring. ...
- Food and Fragrance Analysis. ...
- Pharmaceutical Applications. ...
- Forensic Applications. ...
- Biological Analysis. ...
- Chemical Warfare. ...
- Geochemical Research.
Two types of gas chromatography are encountered: gas-solid chromatography (GSC) and gas-liquid chromatography (GLC). Gas-solid chromatography is based upon a solid stationary phase on which retention of analytes is the consequence of physical adsorption.
Features Gas chromatography
Gas Chromatography Detectors
General-Purpose Detectors. The FID is the most common detector used in gas chromatography. The FID is sensitive to and capable of detecting, compounds that contain carbon atoms (C), which accounts for almost all organic compounds.
Gas Chromatography Injectors
The injector contains a heated chamber containing a glass liner into which the sample is injected through the septum. The carrier gas enters the chamber and can leave by three routes (when the injector is in split mode). The sample vapourises to form a mixture of carrier gas, vapourised solvent, and vapourised solutes.
Gas Chromatography Columns
Two types of columns are used in gas chromatography: packed columns and capillary columns. Short, thick columns made of glass or stainless steel tubes, packed columns have been used since the early stages of gas chromatography.
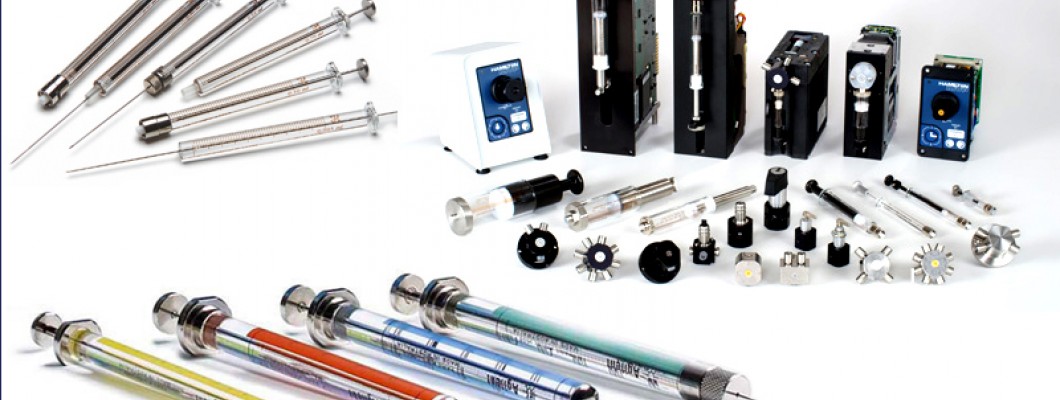
Gas Chromatography Reagents
Chromatography is an analytical technique used in the quantitative determination of the purity of most organic and an increasing number of inorganic reagent chemicals and standard-grade reference materials. The broad scope of chromatography allows it to be used in the separation, identification, and assay of diverse chemical species, ranging from simple metal ions to compounds of complex molecular structure, such as proteins.





Leave a Comment